-
Research Article
-
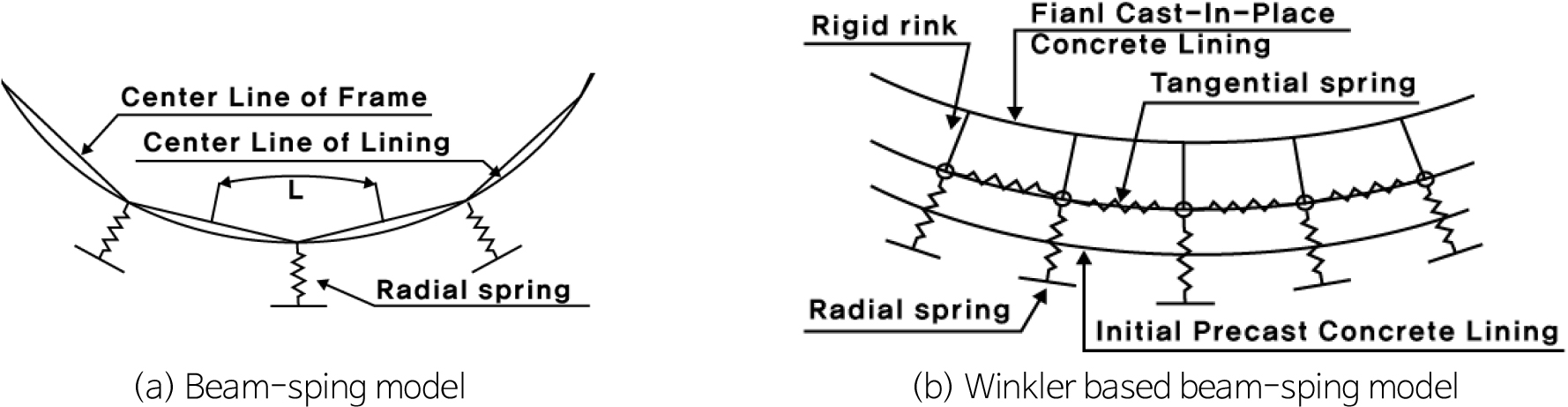
A Study on Design Improved Method for Economical Design of Cast-in-Place Lining for Expressway Tunnel
고속도로 터널 현장타설 라이닝의 경제적인 설계를 위한 설계 개선방안 검토 연구
-
Tae Hyun Lee, Heui Soo Han
이태현, 한희수
-
A Study on Design Improved Method for Economical Design of Cast-in-Place Lining for Expressway Tunnel
-
Research Article
-
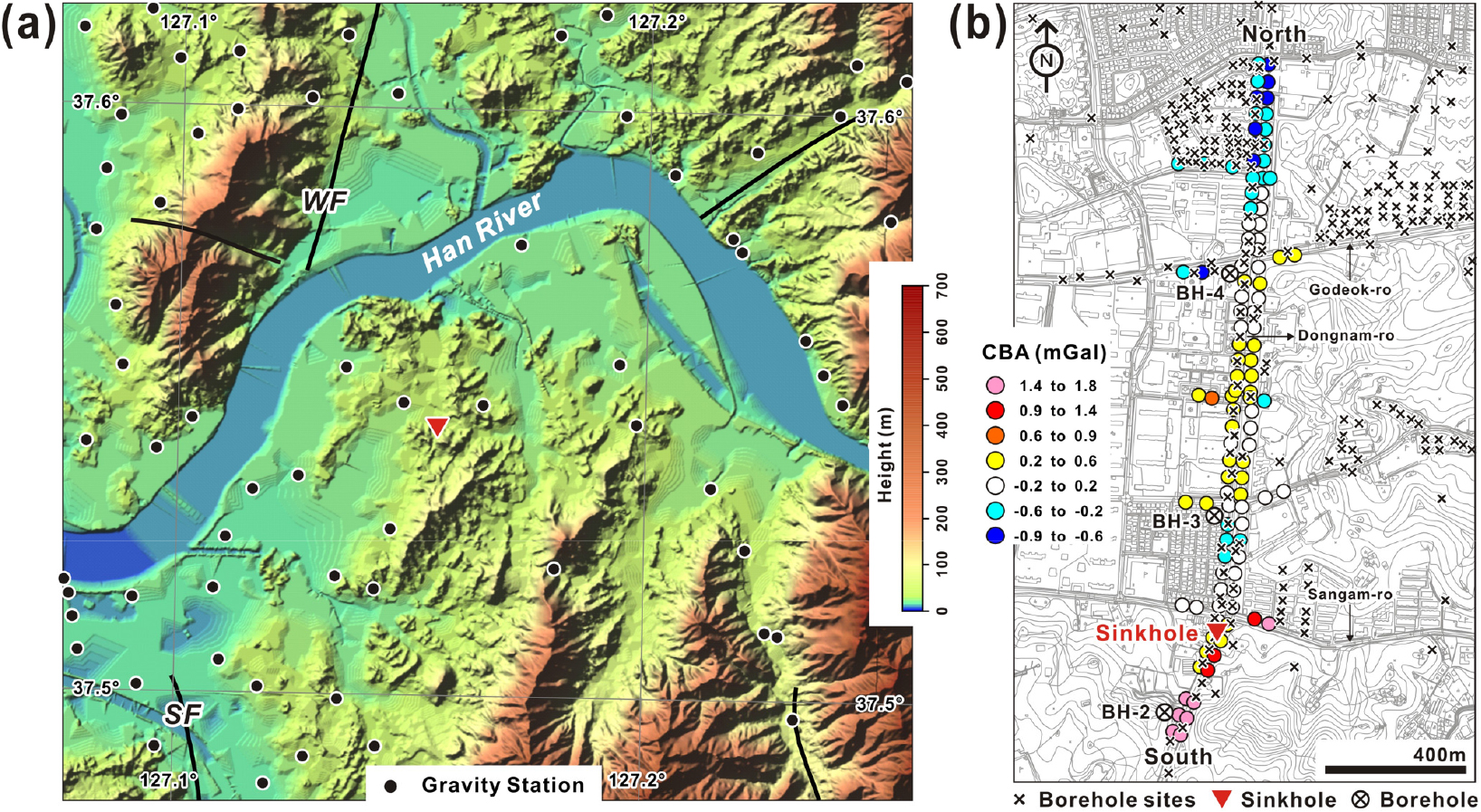
Gravity Field Interpretation and Modeling to Understand the Sinkhole in Myeongil-dong, Gangdong-gu, Seoul
중력장 해석과 수치해석을 통한 서울시 강동구 명일동에서 발생한 땅꺼짐의 원인 고찰
-
Sungchan Choi, Dae-Hong Go, Yeong-Jae Lee, Eun-Kyeong Choi, Sung-Wook Kim
최승찬, 고대홍, 이영재, 최은경, 김성욱
-
Gravity Field Interpretation and Modeling to Understand the Sinkhole in Myeongil-dong, Gangdong-gu, Seoul
-
Research Article
-
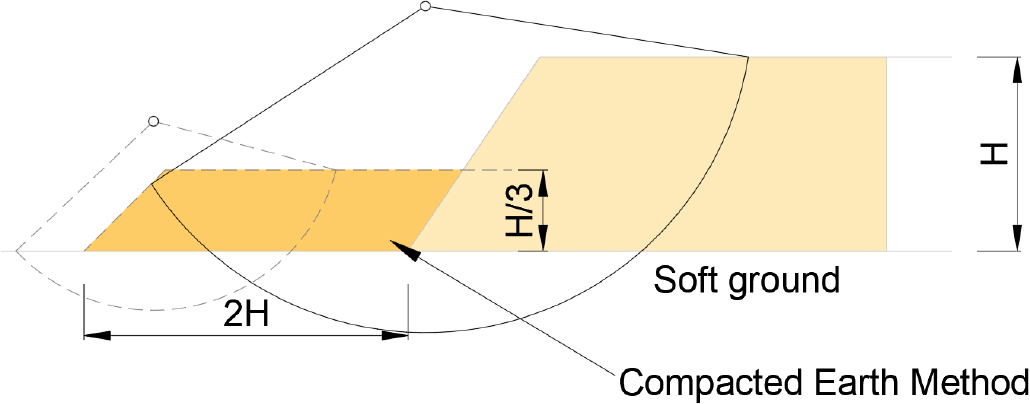
Stability of Landfill Sites Reinforced Using the Compacted Earth Method
압성토로 보강에 따른 폐기물 매립지반의 해석적 검증에 관한 연구
-
Wooyoul Lee, Seokjin Oh, Hyeok Seo
이우열, 오석진, 서 혁
-
Stability of Landfill Sites Reinforced Using the Compacted Earth Method
-
Research Article
-
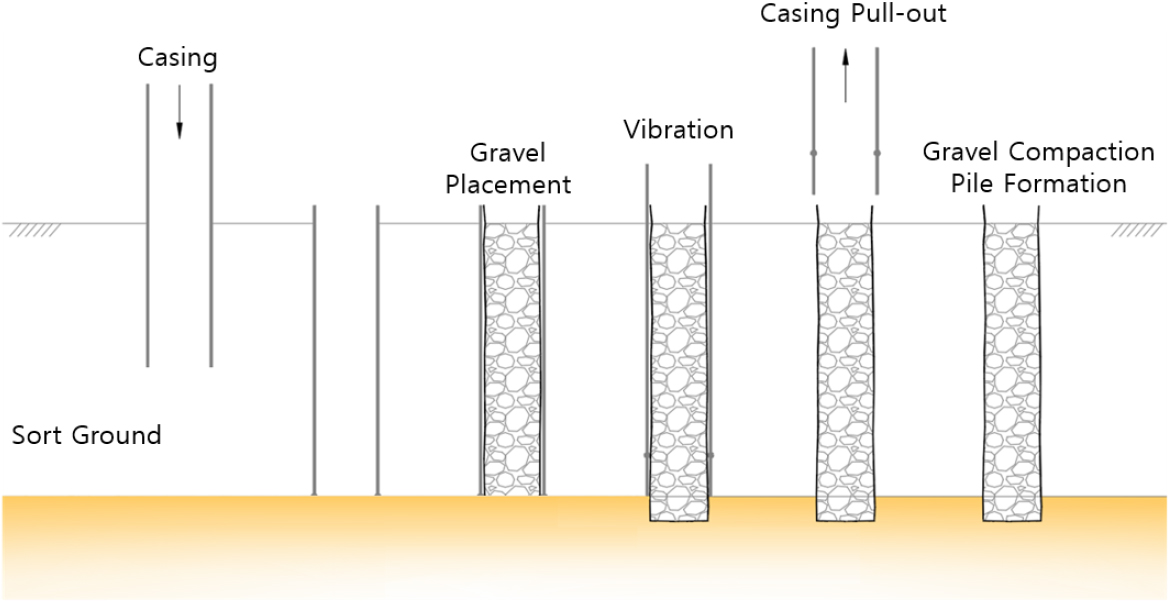
The Dynamic Behavior of Soft Ground Reinforced with Gravel Compaction Piles
쇄석다짐말뚝 보강에 따른 연약지반의 동적 거동특성 분석
-
Seob Lee, Hyeok Seo, Daehyeon Kim
이 섭, 서 혁, 김대현
-
The Dynamic Behavior of Soft Ground Reinforced with Gravel Compaction Piles
-
Research Article
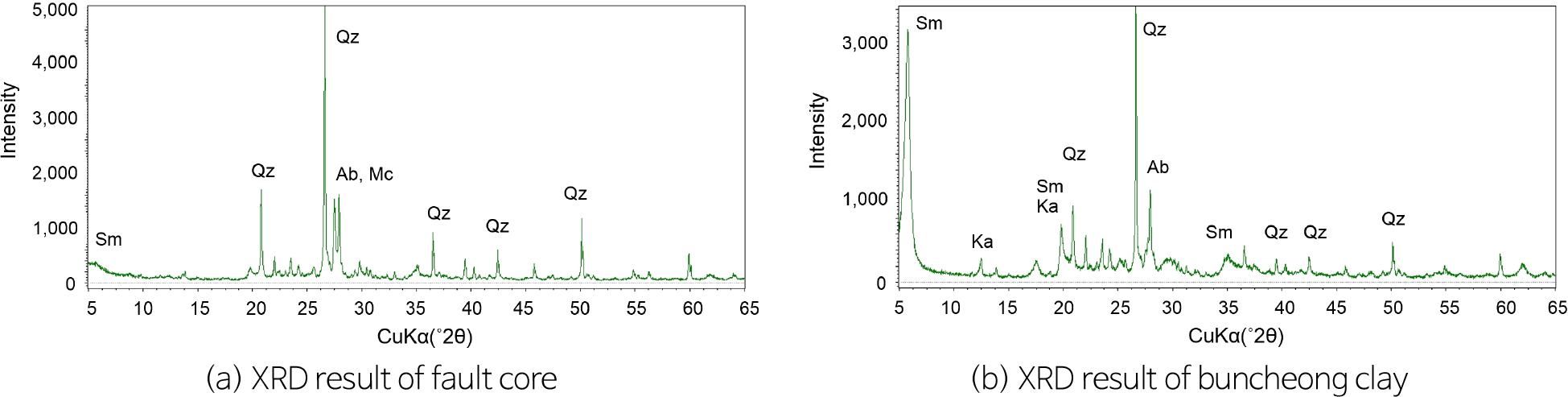
-
Thixotropic Behavior of Artificial Fault Core Specimens with Buncheong Clay
분청토를 이용한 인공 단층핵 시료의 틱소트로피 거동
-
Yu-Jin Ha, Se-Jeong Ju, Hyeong-Sin Kim, MinJi Kang, Yong-Seok Seo
하유진, 주세정, 김형신, 강민지, 서용석
-
Thixotropic Behavior of Artificial Fault Core Specimens with Buncheong Clay
-
Research Article
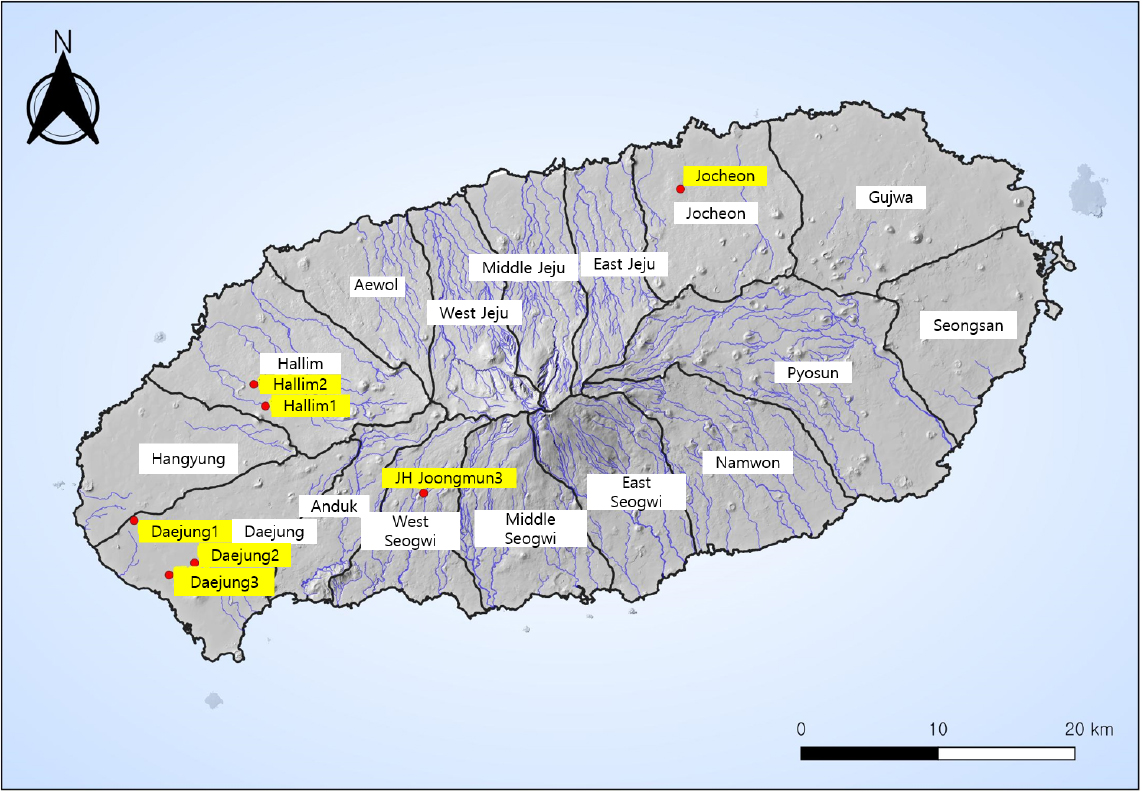
-
Regression Analysis for Predicting Nitrate-N Concentrations in Groundwater in Western Jeju
제주 서부지역 지하수의 질산성질소 농도 예측을 위한 회귀분석
-
Gyu-Han Kim, Hyeong-Sin Kim, Yong-Seok Seo
김규한, 김형신, 서용석
-
Regression Analysis for Predicting Nitrate-N Concentrations in Groundwater in Western Jeju
-
Research Article
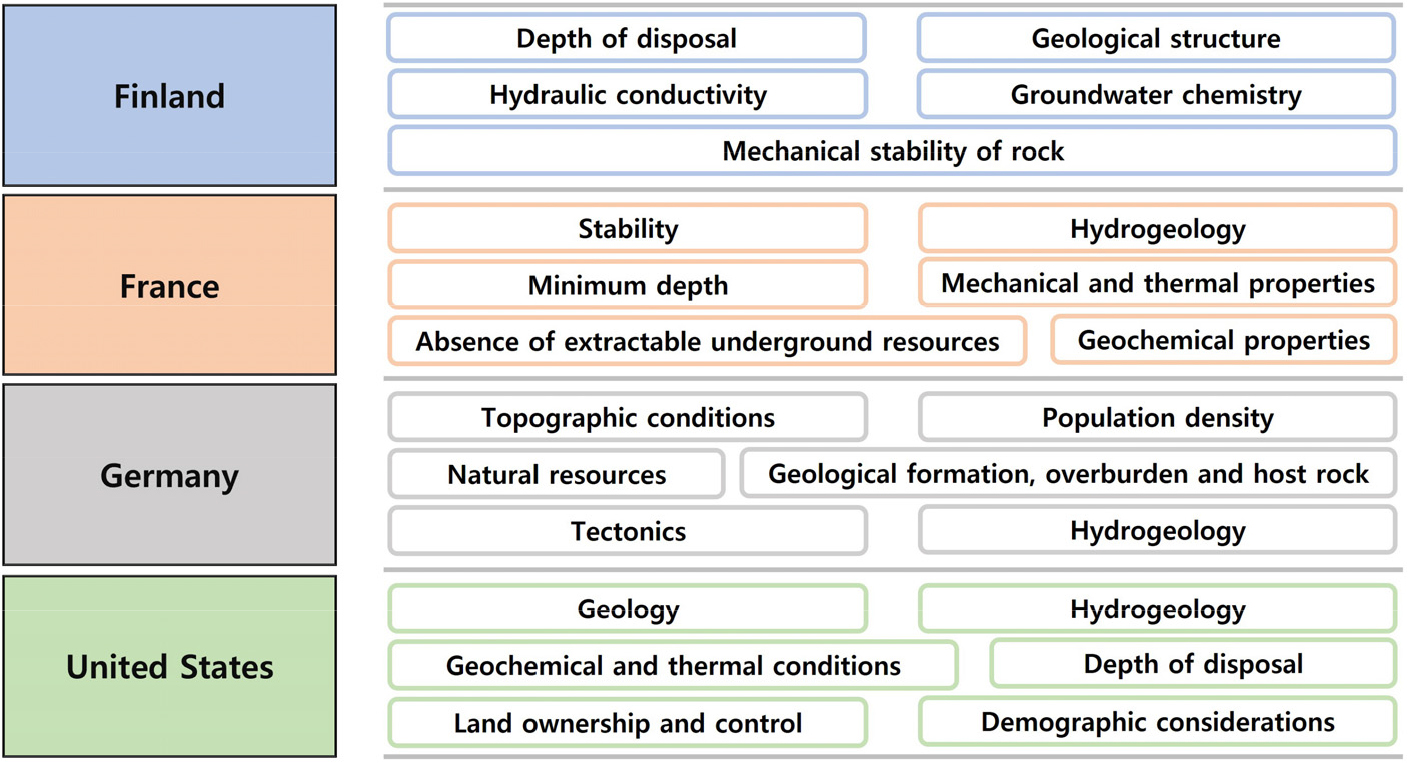
-
Analysis of International Regulatory Requirements for High-Level Radioactive Waste Disposal Sites and Natural Barriers
고준위방사성폐기물 처분 부지 및 천연방벽 규제 요건에 관한 국제 규제 동향 및 분석
-
Taeyoo Na, Byung-Gon Chae
나태유, 채병곤
-
Analysis of International Regulatory Requirements for High-Level Radioactive Waste Disposal Sites and Natural Barriers
-
Research Article
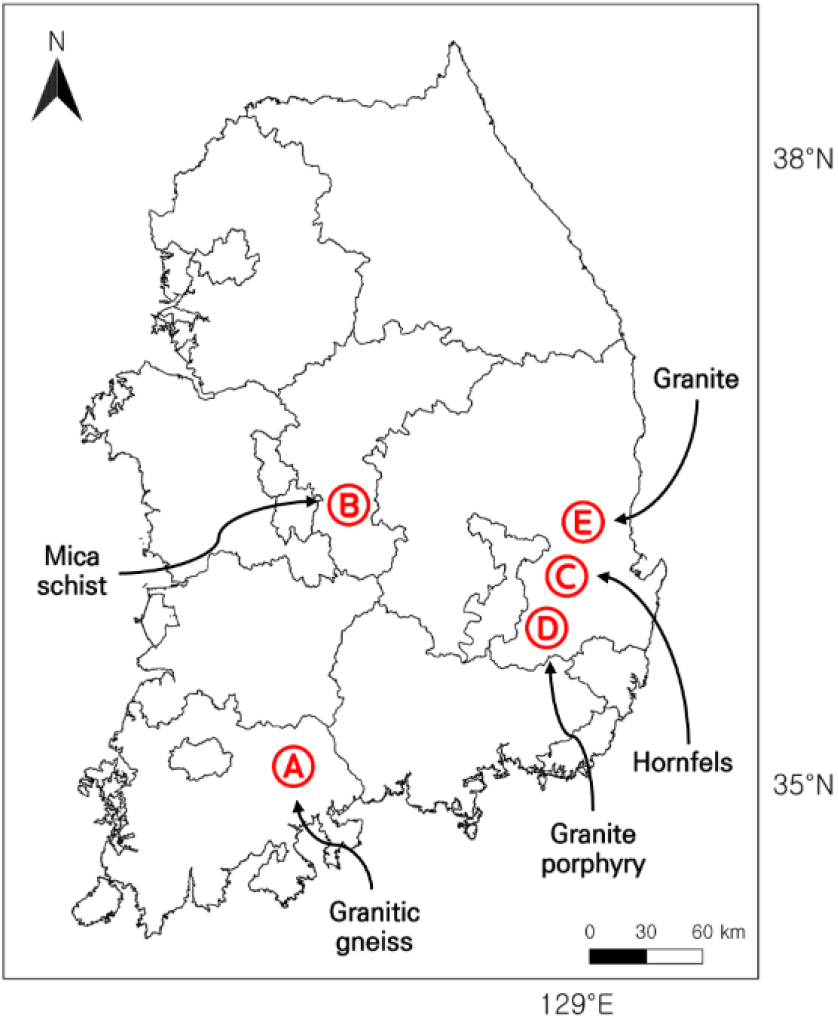
-
Development of Evaluation Indices for Dam-Foundation Grouting Based on Correlation Analysis between Discontinuity and Hydrogeological Parameters across Rock Types
암종별 불연속면 ‧ 수리지질 인자의 상관분석을 통한 댐 기초 그라우팅 평가 지표 제안
-
Kwangmin Beck, Hyerim Lee, Minjune Yang
백광민, 이혜림, 양민준
-
Development of Evaluation Indices for Dam-Foundation Grouting Based on Correlation Analysis between Discontinuity and Hydrogeological Parameters across Rock Types
-
Research Article
-
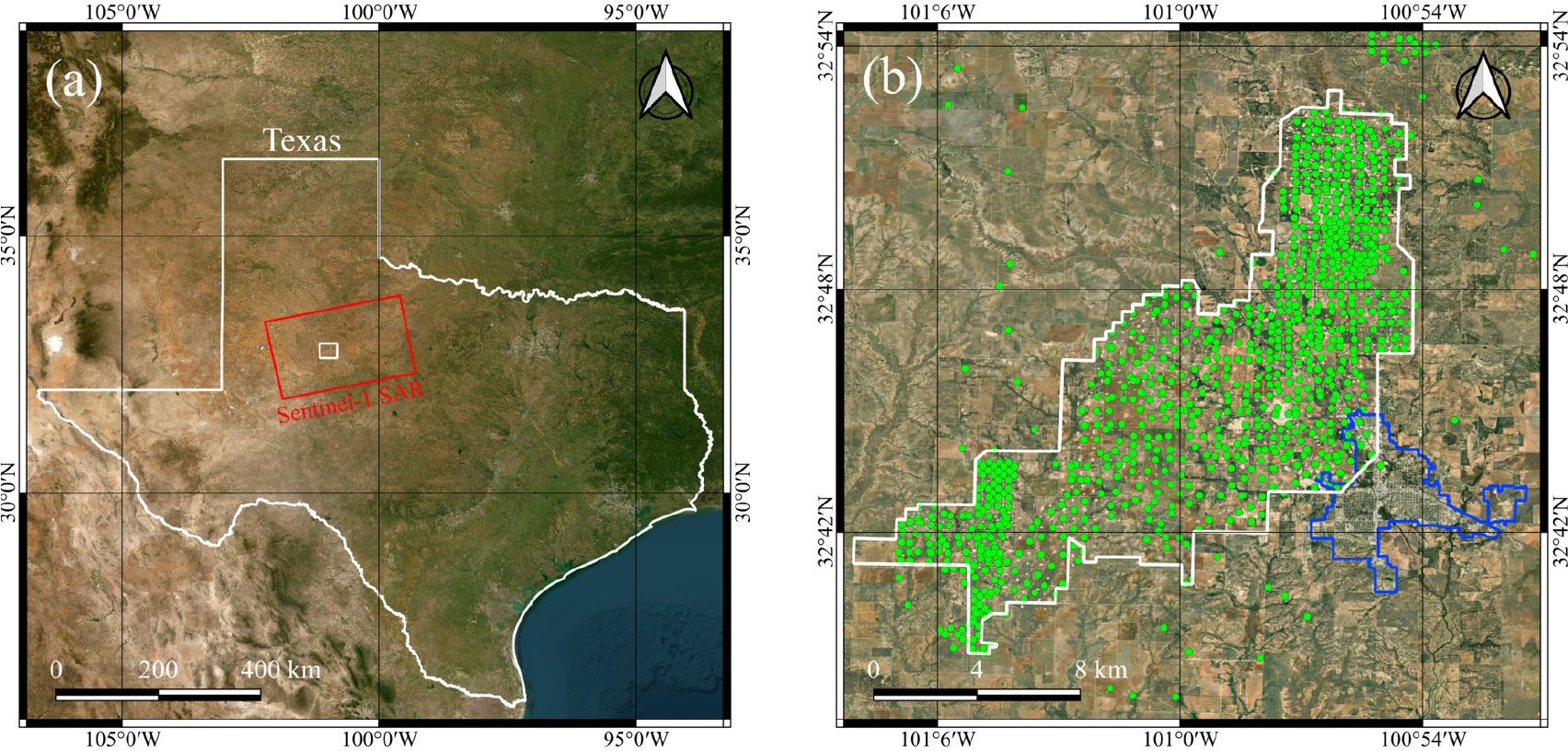
Analysis of Surface Displacement Time-Series Obtained in the SACROC Oil Field during CO2-EOR Using PSInSAR
PSInSAR를 이용한 CO2-EOR이 적용된 SACROC 유전의 시계열 지표변위 분석
-
Junbeom Park, Hyangsun Han, Taewook Kim
박준범, 한향선, 김태욱
-
Analysis of Surface Displacement Time-Series Obtained in the SACROC Oil Field during CO2-EOR Using PSInSAR
Journal Informaiton
 The Journal of Engineering Geology
The Journal of Engineering Geology
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 The Journal of Engineering Geology
The Journal of Engineering Geology











