-
Research Article

-
Long-Term Monitoring and Analysis of Changes in the Soil Layer on Dokdo
장기 모니터링을 통한 독도 자연사면의 토층 변화 분석
-
Kyeong-Su Kim, Young-Suk Song, Dae-Seong Yun, Eunseok Bang
김경수, 송영석, 윤대성, 방은석
- Changes in the soil layer on Dokdo are important both academically and with regard to sustainable conservation and utilization of the islands. …
독도의 토층 변화는 독도에 대한 학술적 가치와 함께 독도의 지속가능한 보전 및 활용 측면에서 상당히 중요한 의미를 가진다. 또한 독도에 자생하는 식물 …
- Changes in the soil layer on Dokdo are important both academically and with regard to sustainable conservation and utilization of the islands. Continuous investigation and observation are necessary, as the soil layer is essential to the growth of plants and, therefore, the islands’ ecosystem. Such work was carried out for about 8 years using soil erosion measuring bars, which are durable and facilitate simple monitoring of changes in the soil layer. Each bar comprised a rod measuring 30~50 cm long and 1.5 cm in diameter, and the use of stainless steel afforded resistance to corrosion caused by sea breezes. Six measuring bars were installed in the soil layers of each of two islands, Dongdo and Seodo, and measurements were taken one to three times a year from 2014 to 2021. The field measurements indicate that soil was deposited on Dongdo but eroded on Seodo during the observation period. As the measuring bars on Dongdo were located in the central and lower parts of the island, the observed changes in the soil layer resulted mainly from sedimentation of material eroded by weathering or soil runoff from the upper part of the island. In contrast, the measurement locations on Seodo were located in the upper and central parts of the island, where soil erosion and runoff diminished the soil layer at the observation points.
- COLLAPSE
독도의 토층 변화는 독도에 대한 학술적 가치와 함께 독도의 지속가능한 보전 및 활용 측면에서 상당히 중요한 의미를 가진다. 또한 독도에 자생하는 식물 및 생물의 발달에 필수적인 토대가 되므로 독도의 토층에 대한 지속적인 조사와 관찰이 필요하다. 따라서, 본 연구에서는 독도의 자연사면에 대한 토층 변화를 측정하기 위하여 내구성이 우수하고 설치 및 관리가 간편하며, 측정이 용이한 지표침식측정계를 설치하였다. 지표침식측정계는 길이 30~50 cm, 직경 1.5 cm의 강봉 형태이며, 해풍으로 인한 부식의 저항성을 높이기 위해 스테인리스 재질로 제작하였다. 그리고 동도와 서도의 토층분포구간을 대상으로 각각 6개씩의 지표침식측정계를 설치하였으며, 2014년부터 2021년까지 약 8년 동안 매년 1회에서 3회의 현장 측정을 실시하였다. 측정결과 지표침식측정계가 설치된 동도의 토층에서는 전반적으로 미세하게 퇴적되는 양상을 보였으며, 서도의 경우 동도와 반대로 미세하게 침식되는 양상이 나타났다. 동도에 설치된 지표침식측정계는 비교적 동도의 중간 혹은 하부지역에 설치되어 있으므로 동도의 토층 변화는 상부에 존재하는 토층에서의 풍화에 의한 침식 혹은 토사유출로 인하여 주로 퇴적되는 양상이 나타났다. 그러나 서도에 설치된 지표침식측정계는 서도의 상부 혹은 중간지역에 설치되어 있으므로 서도의 토층에서는 풍화로 인한 침식 및 유출이 직접 발생되었을 것으로 판단된다.
-
Long-Term Monitoring and Analysis of Changes in the Soil Layer on Dokdo
-
Research Article

- LandScient_EWS: Real-Time Monitoring of Rainfall Thresholds for Landslide Early Warning - A Case Study in the Colombian Andes
- Roberto J. Marin, Julián Camilo Marín-Sánchez
- Landslides pose significant threats to many countries globally, yet the development and implementation of effective landslide early warning systems (LEWS) remain challenging …
- Landslides pose significant threats to many countries globally, yet the development and implementation of effective landslide early warning systems (LEWS) remain challenging due to multifaceted complexities spanning scientific, technological, and political domains. Addressing these challenges demands a holistic approach. Technologically, integrating thresholds, such as rainfall thresholds, with real-time data within accessible, open-source software stands as a promising solution for LEWS. This article introduces LandScient_EWS, a PHP-based program tailored to address this need. The software facilitates the comparison of real-time measured data, such as rainfall, with predefined landslide thresholds, enabling precise calculations and graphical representation of real-time landslide advisory levels across diverse spatial scales, including regional, basin, and hillslope levels. To illustrate its efficacy, the program was applied to a case study in Medellín, Colombia, where a rainfall event on August 26, 2008, triggered a shallow landslide. Through pre-defined rainfall intensity and duration thresholds, the software simulated advisory levels during the recorded rainfall event, utilizing data from a rain gauge positioned within a small watershed and a single grid cell (representing a hillslope) within that watershed. By identifying critical conditions that may lead to landslides in real-time scenarios, LandScient_EWS offers a new paradigm for assessing and responding to landslide hazards, thereby improving the efficiency and effectiveness of LEWS. The findings underscore the software’s potential to streamline the integration of rainfall thresholds into both existing and future landslide early warning systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

-
A Study on the Stability of the Slope according to the Bedding of the Sedimentary Rocks
퇴적암지대의 층리 경사에 따른 비탈면 안정성 검토
-
Seonggi Yu, Chanmook Chung, Dongwon Lee
유성기, 정찬묵, 이동원
- A standard slope stability analysis was undertaken for new railway sections, based on the slope of sedimentary rock layers and filling material …
본 연구는 철도 신설노선 구간 중 퇴적암지대 통과구간의 절토 비탈면 안정성 평가를 위해 퇴적암 층리와 충전물질(샌드심)의 경사에 따른 절토 비탈면의 표준경사 안정성 …
- A standard slope stability analysis was undertaken for new railway sections, based on the slope of sedimentary rock layers and filling material (sand), to evaluate the stability of the cut-off slope in the section passing through a zone of sedimentary rock. The stability analysis was undertaken during the dry and rainy seasons, accounting for earthquake occurrence, based on slope design criteria. It was found that if the slope of the sedimentary rock formation was <10°, the effect on the safety rate of the cut-off slope was insignificant. Furthermore, a slope relief of 1:1.0 or more should be applied with slopes of 10~20°, and 1:1.2 or more with >20°. This study provides an important reference for evaluation of slope stability when railway and road construction is undertaken in areas of sedimentary rock.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 철도 신설노선 구간 중 퇴적암지대 통과구간의 절토 비탈면 안정성 평가를 위해 퇴적암 층리와 충전물질(샌드심)의 경사에 따른 절토 비탈면의 표준경사 안정성 검토를 실시하였다. 안정성 검토는 비탈면 설계 기준에 의해 건기시, 우기시, 지진시로 실시하였다. 그 결과 퇴적암 지층의 경사가 10도 이하일 경우 절토 비탈면 경사에 따른 안전율에 미치는 영향이 미미한 것으로 검토되었다. 또한 10도 초과 20도 미만의 경사에서는 1:1.0 이상, 20도 이상에서는 1:1.2 이상으로 경사완화를 실시하여야 하는 것으로 분석되었다. 본 연구는 추후 철도 및 도로건설이 퇴적암지역에서 이루어질 경우 비탈면 안정성 평가를 위한 중요한 참고자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대한다.
-
A Study on the Stability of the Slope according to the Bedding of the Sedimentary Rocks
-
Research Article

-
Flow Path of Choosan Spring in Nari Basin, Ulleung Island, South Korea
울릉도 나리분지 추산용천수의 유동 경로
-
Byeongdae Lee, Min Han, Dong-Hun Kim, Byong-Wook Cho, Chung-Ryul Ryoo
이병대, 한 민, 김동훈, 조병욱, 류충렬
- This study clarified the flow path of Choosan Spring, Nari Basin, Ulleung Island, South Korea. The orientations of faults and fractures developed …
이 연구는 울릉도 나리분지 추산용천수의 유동 경로를 파악하는 것이다. 칼데라 내부 가장자리를 따라 발달하는 단층과 단열구조들의 발달 방향이 추산용천수 유동 경로에 영향을 …
- This study clarified the flow path of Choosan Spring, Nari Basin, Ulleung Island, South Korea. The orientations of faults and fractures developed on the inner edge of the caldera were identified as major factors affecting the flow path. The main flow paths include fracture zones oriented N-S and E-W. The spring also flows in a NE or NNE direction under the influence of the irregular shape of the caldera, which slopes to the NNE. Using Entrobacteriaceae species as tracers, it was found that Nari groundwater flows toward Choosan Yongchulso. However, the small number of water samples used in the analysis limits our understanding of the flow path from Sungin Valley to Nari Basin and Choosan Yongchulso.
- COLLAPSE
이 연구는 울릉도 나리분지 추산용천수의 유동 경로를 파악하는 것이다. 칼데라 내부 가장자리를 따라 발달하는 단층과 단열구조들의 발달 방향이 추산용천수 유동 경로에 영향을 주는 요소로 파악되었다. 추산용천수는 함양된 지하수가 동서 방향과 남북 방향의 단열대를 따라 추산용출소 방향으로 흐른다. 이와 더불어 북북동 방향으로 경사진 칼데라의 부등함몰의 영향으로 북동 내지 북북동 방향으로 흐르는 것으로 파악되었다. 장내세균과인 Entrobacteriaceae을 이용하여 나리지하수 쪽의 물이 추산용출소 방향으로 유동하는 것으로 파악되었다. 다만, 분석에 사용된 시료수가 매우 적어 성인계곡수로부터 나리분지와 추산용출소까지의 유동경로를 전체적으로 파악할 수 없다는 제한성이 있다.
-
Flow Path of Choosan Spring in Nari Basin, Ulleung Island, South Korea
-
Research Article

-
Determination Method of Suitable Mud Density While Drilling through Confined Aquifer and Its Application
피압대수층을 통과하는 대심도 시추 중 적정이수밀도 결정 방법 및 적용 사례
-
Woon Sang Yoon, Yoosung Kim, Hyeongjin Jeon, Yoonho Song, Changhyun Lee
윤운상, 김유성, 전형진, 송윤호, 이창현
- During deep drilling, confined aquifers can present various challenges such as the inability to remove cuttings, rapid groundwater influx, and mud loss. …
피압대수층은 이를 통과하는 대심도 시추에서 암편 배출 불능, 지하수의 급격한 공내 유입, 이수 손실 등의 문제를 야기한다. 특히 자분 조건일 경우 과압 …
- During deep drilling, confined aquifers can present various challenges such as the inability to remove cuttings, rapid groundwater influx, and mud loss. Particularly in flowing well conditions, it is essential to apply the suitable mud density since the aquifer can generates an overpressurized condition. This paper proposes a method for determining the suitable mud density while drilling (SMD) through confined aquifers using mud window analysis and applies it to a case study. The minimum mud density at each depth, which represents the lower limit of the mud window, is determined by the equivalent mud density pore pressure gradient (or by adding a trip margin) at that depth. The pore pressure gradient of a confined aquifer can be calculated using the piezometric level or well head pressure of the aquifer. As the borehole reaches the confined aquifer, there is a significant increase in pore pressure gradient, which gradually decreases with increasing depth. The SMD to prevent a kick can be determined as the maximum value among the minimum mud densities in the open hole section. After entering the confined aquifer, SMD is maintained as the minimum mud density at the top of the aquifer during the drilling of the open hole section. Additionally, appropriate casing installation can reduce the SMD, minimizing the risk of mud loss or invasion into the highly permeable aquifer.
- COLLAPSE
피압대수층은 이를 통과하는 대심도 시추에서 암편 배출 불능, 지하수의 급격한 공내 유입, 이수 손실 등의 문제를 야기한다. 특히 자분 조건일 경우 과압 공극압이 발생하여 적절한 이수 밀도의 적용이 필수적이다. 이 논문에서는 이수창 분석을 이용하여 피압대수층을 통과하는 시추 중 적정이수밀도(SMD)의 결정방법을 제시하고 이를 사례에 적용하여 적용성을 검토하였다. 심도별 이수창의 하한인 최소이수밀도는 해당 심도의 등가이수밀도 공극압 구배 또는 이에 이송 마진을 더하여 산정되며, 피압대수층의 공극압 구배는 피압지하수위 또는 정두압의 측정으로 구할 수 있다. 시추공이 피압대수층에 도달하면 공극압 구배가 급격히 증가하고, 심도가 증가할 수 록 점차 감소한다. 킥 발생을 방지하기 위한 SMD는 굴진 중인 공저 심도와 그 상부 나공 구간의 최소이수밀도 중 최대값으로 결정할 수 있으며, 피압대수층 진입 이후 SMD는 피압대수층 최상부의 최소이수밀도로서 나공 구간 시추 중 이를 유지하여야 한다. 또한 적절한 케이싱의 설치는 SMD를 낮출 수 있어 고투수성 대수층에 대한 이수 침입 또는 이수 손실의 위험을 감소시킬 수 있다.
-
Determination Method of Suitable Mud Density While Drilling through Confined Aquifer and Its Application
-
Research Article
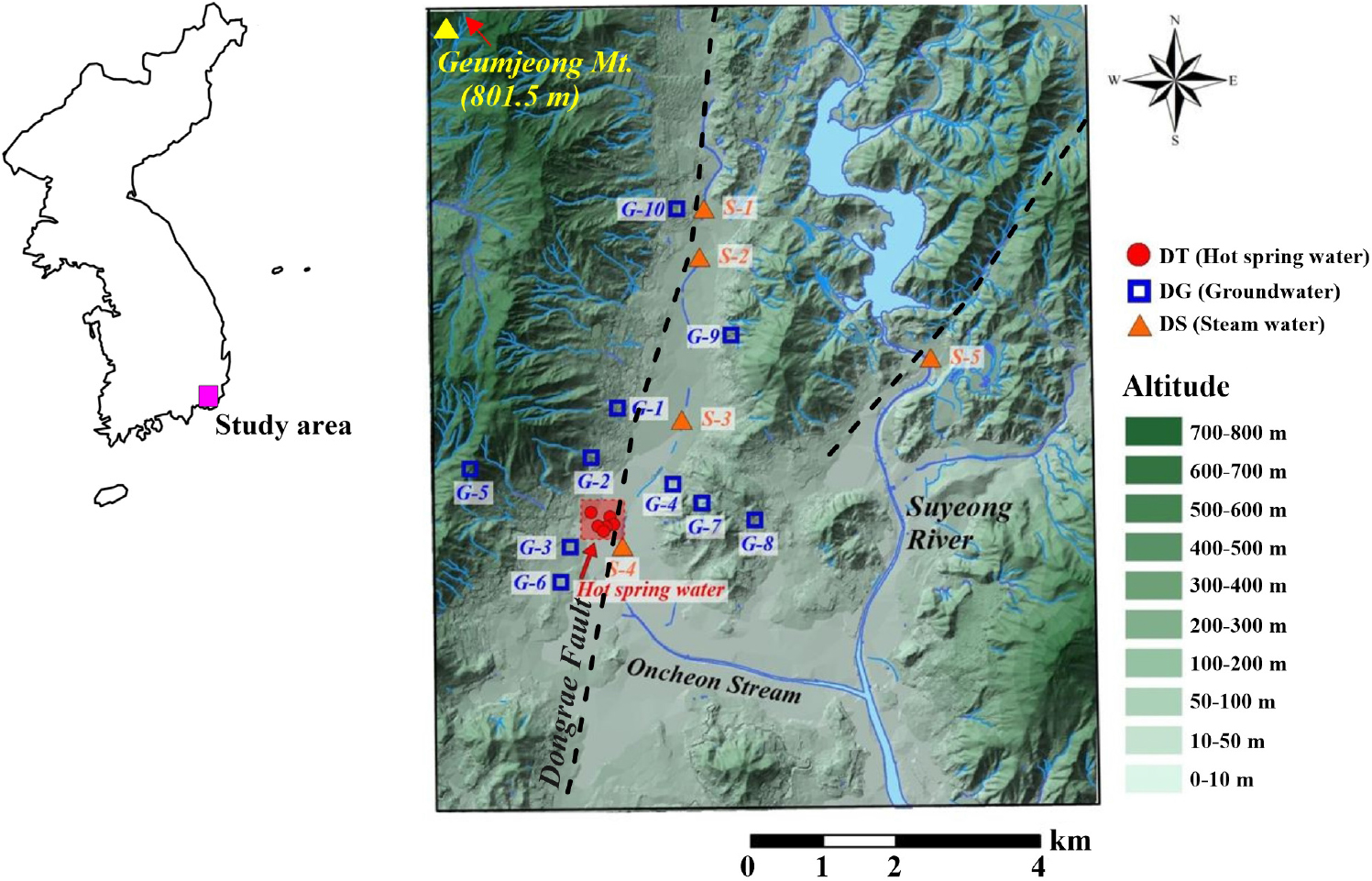
-
Hydrochemistry, Isotopic Characteristics, and Formation Model Geothermal Waters in Dongrae, Busan, South Korea
부산 동래 온천수의 수리화학 및 동위원소 특성, 생성모델 연구
-
Yujin Lee, Chanho Jeong, Yongcheon Lee
이유진, 정찬호, 이용천
- This investigated the hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of geothermal waters, groundwaters, and surface waters in Dongrae-gu, Busan, South Korea, in order to …
연구의 목적은 부산광역시 동래구에서 산출되는 온천수와 주변 지하수 및 지표수의 수리화학 및 동위원소 특성의 규명과 동래 온천수에 함유된 염수 성분의 기원에 대한 …
- This investigated the hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of geothermal waters, groundwaters, and surface waters in Dongrae-gu, Busan, South Korea, in order to determine the origins of the salinity components in the geothermal waters, and their formation mechanisms and heat sources The geothermal waters are Na-Cl-type, distinct from surrounding groundwaters (Na-HCO3- and, Ca-HCO3-(SO4, Cl)-type) and surface waters (Ca-HCO3(SO4, Cl)-type). This indicates the geothermal waters formed at depth as compared with the groundwaters.δ18O and δD values of the geothermal waters are relatively depleted as compared with the groundwaters, due to altitude effects and deep circulation of the geothermal waters. Helium and neon isotope ratios (3He/4He and, 4He/20Ne) of the geothermal waters plot on a single mixing line between mantle (3He = 3.76~4.01%) and crust (4He = 95.99~96.24%), indirectly suggesting that the heat source is due to the decay of radioactive elements in rocks. The geothermal reservoir temperatures were calculated using the silica-enthalpy and Giggenbach models, yielding values of 82~130°C, and the depth of the geothermal reservoir is estimated to be 1.7~2.9 km below the surface. The correlation between Cl/Na and Cl/HCO3 for the Dongrae geothermal waters requires the input of salty water. The supply of saline composition is interpreted due to the dissolution of residual paleo-seawater.
- COLLAPSE
연구의 목적은 부산광역시 동래구에서 산출되는 온천수와 주변 지하수 및 지표수의 수리화학 및 동위원소 특성의 규명과 동래 온천수에 함유된 염수 성분의 기원에 대한 해석, 그리고 온천수의 열원을 포함한 생성 메커니즘을 밝히는 것이다. 동래 온천수의 수리화학적으로 Na-Cl 유형이며, 주변지하수(Na-HCO3, Ca-HCO3(SO4, Cl)), 지표수(Ca-HCO3(SO4, Cl))의 유형과는 다른 형태를 보인다. 이는 지하수에 비해 온천수가 보다 심부의 다른 지화학적 환경에 있음을 지시한다. δ18O와 δD 분석결과 온천수는 지하수에 비해 상대적으로 결핍된 값을 보여주며, 이는 온천수의 함양지역에 대한 고도효과를 반영하고, 온천수의 심부 순환과정을 지시한다. 온천수내 헬륨과 네온 동위원소비(3He/4He, 4He/20Ne)는 맨틀기원(3He = 3.76~4.01%)과 지각기원(4He = 95.99~96.24%) 범위에서 대기기원 헬륨과의 단일혼합선상에 도시되어 온천의 열원이 암석내 방사성물질의 붕괴에 의한 열임을 간접적으로 지시한다. 실리카-엔탈피 모델, Giggenbach 모델 등으로 계산된 지열저장소 온도는 82~130°C의 범위로 계산되었으며, 지열저장소의 깊이는 지표로부터 약 1.7~2.9 km로 계산되었다. 동래 온천수의 Cl/Na 및 Cl/HCO3의 당량비 상관관계는 해수의 혼합영향을 지시하며, 해수의 유입은 잔류고염수의 용해로 해석된다.
-
Hydrochemistry, Isotopic Characteristics, and Formation Model Geothermal Waters in Dongrae, Busan, South Korea
-
Research Article

-
Numerical Analysis of the Stability of a High-Strength Joint Buried Pile Retaining Wall Method
수치해석을 이용한 고강도 결합 매입말뚝 흙막이 공법의 안정성 검토에 관한 연구
-
Hyeok Seo, Yeongpan Ha, Junyoung Choi, Kyungho Park, Daehyeon Kim
서 혁, 하영판, 최준영, 박경호, 김대현
- Retaining walls are widely used in the construction of underground structures. This study reviews the stability of the high-strength joint buried pile …
일반적으로 흙막이 공법은 지하구조물 시공시 주로 사용되는 공법이다. 본 연구에서는 대상현장지반에 대한 고강도 결합 매입말뚝 흙막이 공법의 안정성을 검토하였다. 실험내용으로는 유한요소해석법을 통한 …
- Retaining walls are widely used in the construction of underground structures. This study reviews the stability of the high-strength joint buried pile method at a site in Korea. [Consider giving details of the location.] The method is assessed by considering the amount of ground settlement, as calculated by finite element analysis and measured at the site. Comparison of the measured and numerical results confirmed the method’s stability and field applicability. Settlement of 13.42~13.65 mm was calculated for seven cross-sections [The Abstract should be comprehensible without reference to the main text. The labels A-A′ to G-G′ should not be introduced here without explanation.] using numerical analysis, and the measured settlement reached a maximum of 2.00 mm. The observed differences and variations [Please state what differed/varied.] did not exceed the design expectations in any section. Instruments installed at the back of the excavation area were used to assess the conditions. An underground gradient meter recorded a cumulative horizontal displacement of between -0.40 and 0.60 mm, and an underground water meter recorded slight displacements of between -0.21 and 0.28 m compared with the initial measurements. A surface settlement meter observed very little movement, with a maximum of -2.00 mm compared with the initial measurement, thereby confirming the establishment of a stable state within the management criteria.
- COLLAPSE
일반적으로 흙막이 공법은 지하구조물 시공시 주로 사용되는 공법이다. 본 연구에서는 대상현장지반에 대한 고강도 결합 매입말뚝 흙막이 공법의 안정성을 검토하였다. 실험내용으로는 유한요소해석법을 통한 지반의 침하량 검토를 수행하였으며, 공법이 적용된 지반의 계측 데이터와 수치해석 결과를 비교 ‧ 분석하여 안정성 및 현장 적용성을 확인하고자 하였다. 수치해석상 침하량 결괏값과 현장 계측을 통한 침하량 측정값을 비교한 결과, A-A′~G-G′ 단면의 수치해석상 침하량 결괏값은 최소 13.42 mm~최대 13.65 mm, 현장계측을 통한 침하량은 최대 2.00 mm로 확인되었다. 각각의 오차는 미미한 차이를 보였으며, 모든 구간에서 설계 예상치를 벗어나지 않음을 확인하였다. 굴착주변의 배면에 대한 계측기 설치결과, 지중경사계의 경우 누적수평변위는 -0.40~0.60 mm로 나타났고, 지하수위계 계측결과 초기측정치 대비 -0.21~0.28 m로 미소한 변위를 확인할 수 있었다. 또한 지표침하계의 경우 초기측정치 대비 최대 -2.00 mm로 매우 미소하게 확인되었고, 관리기준 내 안정적인 상태로 확인되었다.
-
Numerical Analysis of the Stability of a High-Strength Joint Buried Pile Retaining Wall Method
-
Research Article

-
Estimation of Groundwater Availability by Using the SWAT-K Model in Yeoncheon District, South Korea
SWAT-K 모형을 이용한 연천지역의 지하수 개발가능량 추정
-
Jeong Eun Lee, Min-Gyu Kim, Il-Moon Chung
이정은, 김민규, 정일문
- The availability of groundwater in the Yeoncheon area, South Korea, was estimated using the distributed hydrological model SWAT-K to calculate recharge rates …
본 연구에서는 연천지역의 개발 가능한 지하수의 양을 추정하기 위해 분포형 수문모형 SWAT-K를 이용하여 토지이용, 토양분포 특성에 따른 함양량을 산정하였다. 모형의 검보정 결과 …
- The availability of groundwater in the Yeoncheon area, South Korea, was estimated using the distributed hydrological model SWAT-K to calculate recharge rates based on land use and soil distribution. Model calibration and validation results were consistent between observed and simulated streamflows, with coefficients of determination of 0.75~0.97. Calculated groundwater recharge rates varied temporospatially, with lower rates in winter and spring than in summer. Estimated recharge rates were compared with the baseflow index of natural streamflow to assess the validity of estimated recharge amounts. Groundwater development potential was determined by calculating the recharge amount for a 10-year period by statistical frequency analysis, confirming it to be 11.5% of annual precipitation.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 연천지역의 개발 가능한 지하수의 양을 추정하기 위해 분포형 수문모형 SWAT-K를 이용하여 토지이용, 토양분포 특성에 따른 함양량을 산정하였다. 모형의 검보정 결과 관측유량과 모의유량의 결정계수가 0.75~0.97로 양호하게 나타났으며 계산된 지하수 함양량은 겨울과 봄에 걸쳐 낮은 함양률을, 여름철에는 높은 함양률을 나타내는 시공간적 특성을 보였다. 계산된 연평균 함양률을 자연유량의 기저유출률과 비교하여 추정된 함양량의 타당성을 검토하였다. 지하수 개발가능량은 통계학적 빈도해석 기법을 이용한 10년 빈도 갈수시의 함양량으로 산정하여 연강수량의 11.5%인 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
-
Estimation of Groundwater Availability by Using the SWAT-K Model in Yeoncheon District, South Korea
-
Research Article

-
Grouting Improvement through Correlation Analysis of Hydrogeology and Discontinuity Factors in a Jointed Rock-Mass
절리 암반의 수리지질 및 불연속면 특성 간 상관분석을 통한 그라우팅 계획 수립의 개선 방안
-
Kwangmin Beck, Seonggan Jang, Seongwoo Jeong, Minjune Yang
백광민, 장성간, 정성우, 양민준
- Large-scale civil engineering structures such as dams require a systematic approach to jointed rock-mass grouting to prevent water leakage into the foundations …
댐은 대규모 토목 구조물로서 안전한 운영을 위해 기초지반의 누수를 차단하고 추가적인 재해를 방지하기 위하여 암반 그라우팅에 대한 체계적인 접근 및 이해가 필요하다. …
- Large-scale civil engineering structures such as dams require a systematic approach to jointed rock-mass grouting to prevent water leakage into the foundations and to ensure safe operation. In South Korea, rock grouting design often relies on the experience of field engineers that was gained in similar projects, highlighting the need for a more systematic and reliable approach. Rock-mass grouting is affected mainly by hydrogeology and the presence of discontinuities, involving factors such as the rock quality designation (RQD), joint spacing (Js), Lugeon value (Lu), and secondary permeability index (SPI). This study, based on data from field investigations of 14 domestic sites, analyzed the correlation between hydrogeological factors (Lu and SPI), discontinuity characteristics (RQD and Js), and grout take, and systematically established a design method for rock grouting. Analysis of correlation between the variables RQD, Js, Lu, and SPI yielded Pearson correlation (r) values as follows: Lu-SPI, 0.92; RQD-Lu, -0.75; RQD-Js, 0.69; RQD-SPI, -0.65; Js-Lu, -0.47; and SPI-Js, -0.41. The grout take increases with Lu and SPI values, but there is no significant correlation between RQD and Js. The proposed approach for grouting design based on SPI values was verified through analysis and comparison with actual curtain-grouting construction, and is expected to be useful in practical applications and future studies.
- COLLAPSE
댐은 대규모 토목 구조물로서 안전한 운영을 위해 기초지반의 누수를 차단하고 추가적인 재해를 방지하기 위하여 암반 그라우팅에 대한 체계적인 접근 및 이해가 필요하다. 국내에서는 암반 그라우팅 계획에 있어 현장 기술자의 경험과 유사 사례에 의존하는 경향이 있으며, 보다 신뢰성 있는 그라우팅 계획을 위해 (토목 or 공학적) 이론과 (현장 or 지반) 조사결과를 바탕으로 한 개선방안이 필요한 실정이다. 암반에서 시행하는 그라우팅은 대부분 수리지질 및 불연속면 인자들(RQD, Js, Lu, SPI)에 의해 가장 큰 영향을 받는다. 본 연구에서는 국내 14개 현장에서 실시된 조사 자료를 토대로 수리지질학적 인자(Lu, SPI)와 불연속면 인자(RQD, Js), 그라우트 주입량(grout take) 간의 상관관계를 분석하고 암반 그라우팅 계획의 체계적인 수립 방안을 제시하였다. 연구 인자(RQD, Js, Lu, SPI) 간의 피어슨 상관계수(r)를 분석한 결과, Lu과 SPI의 상관관계(r = 0.92)가 가장 높고, RQD와 Lu(r = -0.75), RQD와 Js(r = 0.69), RQD와 SPI(r = -0.65), Js와 Lu(r = -0.47), SPI와 Js(r = -0.41) 순으로 상관관계가 감소하는 것으로 나타났다. 그라우트 주입량과 연구 인자(RQD, Js, Lu, SPI) 간 상관관계를 분석한 결과, Lu과 SPI는 값이 커질수록 주입량이 증가하는 경향을 보이나 RQD와 Js는 유의한 상관관계가 나타나지 않았다. SPI를 토대로 제안된 그라우팅 계획 수립의 접근 방법은 실제 수행한 차수 그라우팅 시공 자료와 비교 ‧ 분석을 통해 검증하였고, 향후 세부 연구 및 실무 수행에 있어 유용한 자료로 활용될 수 있다.
-
Grouting Improvement through Correlation Analysis of Hydrogeology and Discontinuity Factors in a Jointed Rock-Mass
-
Technical Note

-
Electrical Resistivity Survey on Paved Surface and Case Studies
포장된 지표에서의 전기비저항 탐사 및 사례 연구
-
Juyeon Jeong, Myungjin Nam
정주연, 남명진
- Urban development and the expansion of electrical resistivity surveying applications have increased the need for soil and underground structure investigations on paved …
최근 도심지의 발달과 전기비저항 탐사 적용 분야 및 현장의 확대에 따라, 포장된 지표에서 토양이나 지하 구조를 조사하기 위한 탐사의 필요성이 증가하고 있다. …
- Urban development and the expansion of electrical resistivity surveying applications have increased the need for soil and underground structure investigations on paved surfaces. Traditional methods involved drilling through the pavement or surveying surrounding soil. Recently, non-invasive surveying techniques have been developed. This paper analyzes these methods, categorizing them into galvanic methods (including drilling and flat ground electrodes) and capacitive coupling methods. By examining case studies, it suggests selecting the appropriate method based on the pros and cons of each and the specific site characteristics. The paper also discusses the applicability and limitations of electrical resistivity surveying through various examples.
- COLLAPSE
최근 도심지의 발달과 전기비저항 탐사 적용 분야 및 현장의 확대에 따라, 포장된 지표에서 토양이나 지하 구조를 조사하기 위한 탐사의 필요성이 증가하고 있다. 과거에는 포장된 표면에서의 탐사는 포장재를 천공하거나 그 주변의 토양에서의 탐사로 대체하였다. 최근 포장재를 손상하지 않고 포장된 지표에서 탐사하는 방법 및 연구 사례들이 늘어남에 따라, 이 논문에서는 이에 대해 분석하고자 한다. 포장 지표에서의 전기비저항 탐사 방법을 기존의 천공 후 전극 삽입 방법, 평판 접지 전극 사용을 포함한 갈바닉 방법과 용량성 결합 방식으로 나누어 각 방법의 적용 사례를 조사하였다. 이를 통해 각 탐사 방법의 장단점과 탐사 현장의 특성을 고려하여 적절한 탐사 방법을 선택할 수 있음을 시사하였다. 마지막으로, 전기비저항 탐사의 적용 가능성과 한계를 다양한 사례를 통해 분석하였습니다.
-
Electrical Resistivity Survey on Paved Surface and Case Studies
-
Technical Note

-
The Effect of the Discontinuity Spacing/Length Ratio on Step-Path Failure of Jointed Rock Slopes
절리 암반 사면의 계단 경로 파괴에 미치는 불연속면 간격/길이 비의 영향
-
Woon Sang Yoon
윤운상
- When a non-persistent joint system is formed in a large-scale rock slope, slope failure may occur due to presence of a the …
대규모 암반 사면에서 비연속성의 절리계가 발달할 때, 계단상 활동면에 의한 사면 파괴가 발생할 수 있다. 계단상 활동면은 절리-절리 활동면 또는 절리-암교 활동면으로 …
- When a non-persistent joint system is formed in a large-scale rock slope, slope failure may occur due to presence of a the stepped sliding surface. Such a surface can be divided into joint-to-joint sliding surfaces or joint-to-rock bridge sliding surfaces. In the latter case, the rock bridge provides shear resistance parallel to the joint and tensile resistance perpendicular to the joint. The load of the sliding rock can lead to failure of the rock bridge, thereby connecting the two joints at each ends of the bridge and resulting in step-path failure of the slope. If each rock bridge on a slope has the same length, the tensile strength is lower than the shear strength, resulting in the rock bridges oriented perpendicular to the joint being more prone to failure. In addition, the smaller the ratio of discontinuity spacing to length, the greater the likelihood of step-path failure. To assess the risk of stepped sliding on a rock slope with non-persistent joints, stability analysis can be performed using limit equilibrium analysis or numerical analysis. This involves constructing a step-path failure surface through a systematic discontinuity survey and analysis.
- COLLAPSE
대규모 암반 사면에서 비연속성의 절리계가 발달할 때, 계단상 활동면에 의한 사면 파괴가 발생할 수 있다. 계단상 활동면은 절리-절리 활동면 또는 절리-암교 활동면으로 구분할 수 있으며, 절리-암교 활동면에서 암교는 절리와 평행한 전단 저항과 절리에 수직인 인장 저항을 제공한다. 계단 경로 파괴는 활동 암괴의 하중에 의해 암교의 파괴가 발생하여 암교 양단의 두 절리가 연결되며 발생한다. 암교의 길이가 동일하다면 암석의 인장강도가 전단강도에 비해 낮으므로 절리에 수직으로 형성된 암교가 파괴에 취약하며, 불연속면 간격/길이의 비가 작을수록 계단 경로 파괴의 가능성이 커진다. 비연속성의 절리가 발달하는 암반 사면의 계단상 활동 파괴 위험에 대한 평가를 위해서는 체계적인 불연속면 조사 및 분석을 통해 계단 경로 파괴면을 구성하여 한계 평형 해석 또는 수치 해석 등의 안정성 평가를 수행하여야 한다.
-
The Effect of the Discontinuity Spacing/Length Ratio on Step-Path Failure of Jointed Rock Slopes
-
Technical Note

-
Hydrological Drought Evaluation in Upstream Inje Region
인제지역의 수문학적 가뭄 평가
-
Joo-Heon Lee, Min-Gyu Kim, Si-Jung Choi, Il-Moon Chung
이주헌, 김민규, 최시중, 정일문
- In this study, drought assessment using the standardized precipitation index (SPI) and streamflow drought index (SDI) was conducted for the Inje region, …
본 연구에서는 인제 지역에 대해 표준강수지수(SPI), 수문학적 가뭄지수(SDI)를 이용한 가뭄 평가를 수행하였다. 가뭄 분석을 위한 기초자료(강우, 유량) 자료 등을 통해서 월별 유량 …
- In this study, drought assessment using the standardized precipitation index (SPI) and streamflow drought index (SDI) was conducted for the Inje region, Gangwon Province, South Korea. Monthly streamflow ratios were reviewed through basic data for drought analysis (rainfall, streamflow), and meteorological drought and hydrological drought analysis were conducted using precipitation and water level/flow observation stations near the Inje watershed. The analysis revealed that the drought that occurred in 2014 persisted until 2017 consistently across all drought indices (SPI, SDI). When analyzing drought indices calculated using 12 months of hydrometeorological data, it was found that severe drought lasted for approximately 24 months, indicating that drought damage would have been severe.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 인제 지역에 대해 표준강수지수(SPI), 수문학적 가뭄지수(SDI)를 이용한 가뭄 평가를 수행하였다. 가뭄 분석을 위한 기초자료(강우, 유량) 자료 등을 통해서 월별 유량 비율 등을 검토하였고, 인제군 유역 인근의 강수 및 수위/유량 관측소를 활용하여 기상학적 가뭄 및 수문학적 가뭄분석을 진행한 결과 모든 가뭄지수(SPI, SDI)에서 공통적으로 2014년에 발생한 가뭄이 2017년까지 지속되었던 것으로 분석되었다. 지속기간 12개월의 수문기상자료를 활용하여 가뭄지수를 산정하여 분석한 경우, 심한가뭄 지속기간이 24개월 정도 지속되었던 것으로 확인되었으며 따라서 가뭄으로 인한 피해가 극심했을 것으로 평가된다.
-
Hydrological Drought Evaluation in Upstream Inje Region
Journal Informaiton
 The Journal of Engineering Geology
The Journal of Engineering Geology
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 The Journal of Engineering Geology
The Journal of Engineering Geology









